Small Bowel Obstruction Due to Infraumbilical Hernia
Article Information
Vikas Bhatia MD*, DNB, DM, Lokesh Singh MD*, Jyoti Gupta MD, Uma Debi MD
Department of Radio diagnosis, PGIMER Chandigarh, India
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Vikas Bhatia, Department of Radio diagnosis, PGIMER Chandigarh, India
Received: 14 March 2020; Accepted: 02 April 2020; Published: 09 April 2020
Citation: Vikas Bhatia MD, DNB, DM, Lokesh Singh MD, Jyoti Gupta MD, Uma Debi M. Small Bowel Obstruction Due to Infraumbilical Hernia. Journal of Radiology and Clinical Imaging 3 (2020): 048-049.
Share at FacebookKeywords
Small bowel obstruction; Infraumbilical; Computed tomography
Small bowel obstruction articles, Infraumbilical articles, Computed tomography articles
Small bowel obstruction articles Small bowel obstruction Research articles Small bowel obstruction review articles Small bowel obstruction PubMed articles Small bowel obstruction PubMed Central articles Small bowel obstruction 2023 articles Small bowel obstruction 2024 articles Small bowel obstruction Scopus articles Small bowel obstruction impact factor journals Small bowel obstruction Scopus journals Small bowel obstruction PubMed journals Small bowel obstruction medical journals Small bowel obstruction free journals Small bowel obstruction best journals Small bowel obstruction top journals Small bowel obstruction free medical journals Small bowel obstruction famous journals Small bowel obstruction Google Scholar indexed journals Infraumbilical articles Infraumbilical Research articles Infraumbilical review articles Infraumbilical PubMed articles Infraumbilical PubMed Central articles Infraumbilical 2023 articles Infraumbilical 2024 articles Infraumbilical Scopus articles Infraumbilical impact factor journals Infraumbilical Scopus journals Infraumbilical PubMed journals Infraumbilical medical journals Infraumbilical free journals Infraumbilical best journals Infraumbilical top journals Infraumbilical free medical journals Infraumbilical famous journals Infraumbilical Google Scholar indexed journals Computed tomography articles Computed tomography Research articles Computed tomography review articles Computed tomography PubMed articles Computed tomography PubMed Central articles Computed tomography 2023 articles Computed tomography 2024 articles Computed tomography Scopus articles Computed tomography impact factor journals Computed tomography Scopus journals Computed tomography PubMed journals Computed tomography medical journals Computed tomography free journals Computed tomography best journals Computed tomography top journals Computed tomography free medical journals Computed tomography famous journals Computed tomography Google Scholar indexed journals Infraumbilical Hernia articles Infraumbilical Hernia Research articles Infraumbilical Hernia review articles Infraumbilical Hernia PubMed articles Infraumbilical Hernia PubMed Central articles Infraumbilical Hernia 2023 articles Infraumbilical Hernia 2024 articles Infraumbilical Hernia Scopus articles Infraumbilical Hernia impact factor journals Infraumbilical Hernia Scopus journals Infraumbilical Hernia PubMed journals Infraumbilical Hernia medical journals Infraumbilical Hernia free journals Infraumbilical Hernia best journals Infraumbilical Hernia top journals Infraumbilical Hernia free medical journals Infraumbilical Hernia famous journals Infraumbilical Hernia Google Scholar indexed journals Radiological impression articles Radiological impression Research articles Radiological impression review articles Radiological impression PubMed articles Radiological impression PubMed Central articles Radiological impression 2023 articles Radiological impression 2024 articles Radiological impression Scopus articles Radiological impression impact factor journals Radiological impression Scopus journals Radiological impression PubMed journals Radiological impression medical journals Radiological impression free journals Radiological impression best journals Radiological impression top journals Radiological impression free medical journals Radiological impression famous journals Radiological impression Google Scholar indexed journals Image articles Image Research articles Image review articles Image PubMed articles Image PubMed Central articles Image 2023 articles Image 2024 articles Image Scopus articles Image impact factor journals Image Scopus journals Image PubMed journals Image medical journals Image free journals Image best journals Image top journals Image free medical journals Image famous journals Image Google Scholar indexed journals strangulation articles strangulation Research articles strangulation review articles strangulation PubMed articles strangulation PubMed Central articles strangulation 2023 articles strangulation 2024 articles strangulation Scopus articles strangulation impact factor journals strangulation Scopus journals strangulation PubMed journals strangulation medical journals strangulation free journals strangulation best journals strangulation top journals strangulation free medical journals strangulation famous journals strangulation Google Scholar indexed journals incarceration articles incarceration Research articles incarceration review articles incarceration PubMed articles incarceration PubMed Central articles incarceration 2023 articles incarceration 2024 articles incarceration Scopus articles incarceration impact factor journals incarceration Scopus journals incarceration PubMed journals incarceration medical journals incarceration free journals incarceration best journals incarceration top journals incarceration free medical journals incarceration famous journals incarceration Google Scholar indexed journals omental fat articles omental fat Research articles omental fat review articles omental fat PubMed articles omental fat PubMed Central articles omental fat 2023 articles omental fat 2024 articles omental fat Scopus articles omental fat impact factor journals omental fat Scopus journals omental fat PubMed journals omental fat medical journals omental fat free journals omental fat best journals omental fat top journals omental fat free medical journals omental fat famous journals omental fat Google Scholar indexed journals properitoneal fat articles properitoneal fat Research articles properitoneal fat review articles properitoneal fat PubMed articles properitoneal fat PubMed Central articles properitoneal fat 2023 articles properitoneal fat 2024 articles properitoneal fat Scopus articles properitoneal fat impact factor journals properitoneal fat Scopus journals properitoneal fat PubMed journals properitoneal fat medical journals properitoneal fat free journals properitoneal fat best journals properitoneal fat top journals properitoneal fat free medical journals properitoneal fat famous journals properitoneal fat Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Clinical Image
A 68 year old obese female patient presented to emergency department with a hard palapable lump in periumbilical region for last 7 days. She complains of recurrent vomiting with constipation and obstipation for last three days. Clinical examination revealed an approximately 5 × 8 cms sized, firm, smooth marginated, nontender, non yielding mass in infraumbilical region (arrow; Figure 1A) which does not reduce on pressing. No gurgling sound heard on auscultation. Contrast enhanced CT scan revealed presence of an approximately 2.6 cms sized ventral defect in abdominal wall in left para median infraumbilical location through which small bowel (distal jejunal loop), omental fat and properitoneal fat herniated out into a sac measuring 5 × 7 × 9 cms in AP × TR × CC dimensions (arrow; Figure 1B). There was twisting of bowel loop at neck of sac and proximal dilatation of duodenojejunal loops. Mild mural thickening was seen herniated bowel loop with adjacent fat stranding. No fluid collection within the sac. Distal bowel loops were predominantly collapsed. Radiological impression of a ventral incarcerated hernia with proximal small bowel obstruction was made. Abdominal wall hernias are commonly complicated by strangulation or incarceration. Early diagnosis of these complications is important to ensure early management. Multi-detector row computed tomography (CT) is particularly useful for the evaluation of these hernias and associated complications due to its multiplanar capabilities [1, 2].
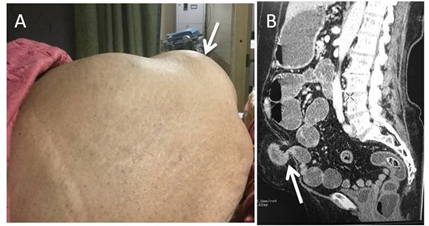
Figure 1A: Hard palpable lump in infraumbilical region.
Figure 1B: Ventral defect in abdominal wall in left para median infraumbilical location through which small bowel (distal jejunal loop), omental fat and properitoneal fat herniated out into a sac.
Patient Consent
Informed consent was taken from the patient
Conflicts of Interest and Funding
Nil
References
- Aguirre DA, Casola G, Sirlin C. Abdominal wall hernias: MDCT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183 (2004): 681-690.
- Zalcman M, Sy M, Donckier V, et al. Helical CT signs in the diagnosis of intestinal ischemia in small-bowel obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 175 (2000): 1601-1607.
