Pancreas Bifidum As Predisposing Factor for Acute Pancreatitis
Article Information
Antonio Pierro*
Radiology Department, Gemelli Molise Hospital, Campobasso, Italy
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Antonio Pierro, Radiology Department, Gemelli Molise Hospital, Campobasso, Italy
Received: 20 November 2020; Accepted: 30 November 2020; Published: 04 December 2020
Citation: Antonio Pierro. Pancreas Bifidum As Predisposing Factor for Acute Pancreatitis. Journal of Radiology and Clinical Imaging 3 (2020): 096-098.
Share at FacebookKeywords
Bifid tail of pancreas; Fish tail pancreas; Branching of the main pancreatic duct
Bifid tail of pancreas articles; Fish tail pancreas articles; Branching of the main pancreatic duct articles
Bifid tail of pancreas articles Bifid tail of pancreas Research articles Bifid tail of pancreas review articles Bifid tail of pancreas PubMed articles Bifid tail of pancreas PubMed Central articles Bifid tail of pancreas 2023 articles Bifid tail of pancreas 2024 articles Bifid tail of pancreas Scopus articles Bifid tail of pancreas impact factor journals Bifid tail of pancreas Scopus journals Bifid tail of pancreas PubMed journals Bifid tail of pancreas medical journals Bifid tail of pancreas free journals Bifid tail of pancreas best journals Bifid tail of pancreas top journals Bifid tail of pancreas free medical journals Bifid tail of pancreas famous journals Bifid tail of pancreas Google Scholar indexed journals Fish tail pancreas articles Fish tail pancreas Research articles Fish tail pancreas review articles Fish tail pancreas PubMed articles Fish tail pancreas PubMed Central articles Fish tail pancreas 2023 articles Fish tail pancreas 2024 articles Fish tail pancreas Scopus articles Fish tail pancreas impact factor journals Fish tail pancreas Scopus journals Fish tail pancreas PubMed journals Fish tail pancreas medical journals Fish tail pancreas free journals Fish tail pancreas best journals Fish tail pancreas top journals Fish tail pancreas free medical journals Fish tail pancreas famous journals Fish tail pancreas Google Scholar indexed journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct articles Branching of the main pancreatic duct Research articles Branching of the main pancreatic duct review articles Branching of the main pancreatic duct PubMed articles Branching of the main pancreatic duct PubMed Central articles Branching of the main pancreatic duct 2023 articles Branching of the main pancreatic duct 2024 articles Branching of the main pancreatic duct Scopus articles Branching of the main pancreatic duct impact factor journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct Scopus journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct PubMed journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct medical journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct free journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct best journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct top journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct free medical journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct famous journals Branching of the main pancreatic duct Google Scholar indexed journals Acute Pancreatitis articles Acute Pancreatitis Research articles Acute Pancreatitis review articles Acute Pancreatitis PubMed articles Acute Pancreatitis PubMed Central articles Acute Pancreatitis 2023 articles Acute Pancreatitis 2024 articles Acute Pancreatitis Scopus articles Acute Pancreatitis impact factor journals Acute Pancreatitis Scopus journals Acute Pancreatitis PubMed journals Acute Pancreatitis medical journals Acute Pancreatitis free journals Acute Pancreatitis best journals Acute Pancreatitis top journals Acute Pancreatitis free medical journals Acute Pancreatitis famous journals Acute Pancreatitis Google Scholar indexed journals Predisposing Factor articles Predisposing Factor Research articles Predisposing Factor review articles Predisposing Factor PubMed articles Predisposing Factor PubMed Central articles Predisposing Factor 2023 articles Predisposing Factor 2024 articles Predisposing Factor Scopus articles Predisposing Factor impact factor journals Predisposing Factor Scopus journals Predisposing Factor PubMed journals Predisposing Factor medical journals Predisposing Factor free journals Predisposing Factor best journals Predisposing Factor top journals Predisposing Factor free medical journals Predisposing Factor famous journals Predisposing Factor Google Scholar indexed journals MR cholangiopancreatography articles MR cholangiopancreatography Research articles MR cholangiopancreatography review articles MR cholangiopancreatography PubMed articles MR cholangiopancreatography PubMed Central articles MR cholangiopancreatography 2023 articles MR cholangiopancreatography 2024 articles MR cholangiopancreatography Scopus articles MR cholangiopancreatography impact factor journals MR cholangiopancreatography Scopus journals MR cholangiopancreatography PubMed journals MR cholangiopancreatography medical journals MR cholangiopancreatography free journals MR cholangiopancreatography best journals MR cholangiopancreatography top journals MR cholangiopancreatography free medical journals MR cholangiopancreatography famous journals MR cholangiopancreatography Google Scholar indexed journals MRI articles MRI Research articles MRI review articles MRI PubMed articles MRI PubMed Central articles MRI 2023 articles MRI 2024 articles MRI Scopus articles MRI impact factor journals MRI Scopus journals MRI PubMed journals MRI medical journals MRI free journals MRI best journals MRI top journals MRI free medical journals MRI famous journals MRI Google Scholar indexed journals clinical image articles clinical image Research articles clinical image review articles clinical image PubMed articles clinical image PubMed Central articles clinical image 2023 articles clinical image 2024 articles clinical image Scopus articles clinical image impact factor journals clinical image Scopus journals clinical image PubMed journals clinical image medical journals clinical image free journals clinical image best journals clinical image top journals clinical image free medical journals clinical image famous journals clinical image Google Scholar indexed journals pancreas bifidum articles pancreas bifidum Research articles pancreas bifidum review articles pancreas bifidum PubMed articles pancreas bifidum PubMed Central articles pancreas bifidum 2023 articles pancreas bifidum 2024 articles pancreas bifidum Scopus articles pancreas bifidum impact factor journals pancreas bifidum Scopus journals pancreas bifidum PubMed journals pancreas bifidum medical journals pancreas bifidum free journals pancreas bifidum best journals pancreas bifidum top journals pancreas bifidum free medical journals pancreas bifidum famous journals pancreas bifidum Google Scholar indexed journals Axial T2-weighted image articles Axial T2-weighted image Research articles Axial T2-weighted image review articles Axial T2-weighted image PubMed articles Axial T2-weighted image PubMed Central articles Axial T2-weighted image 2023 articles Axial T2-weighted image 2024 articles Axial T2-weighted image Scopus articles Axial T2-weighted image impact factor journals Axial T2-weighted image Scopus journals Axial T2-weighted image PubMed journals Axial T2-weighted image medical journals Axial T2-weighted image free journals Axial T2-weighted image best journals Axial T2-weighted image top journals Axial T2-weighted image free medical journals Axial T2-weighted image famous journals Axial T2-weighted image Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Main Point
This paper would like to present one of the possible causes of recurrent acute pancreatitis, namely the bifid pancreas. This anatomical variant is best investigated only with the abdominal MRI, including MRCP (MR cholangiopancreatography).
2. Clinical Image
Bifid tail of pancreas (fish tail pancreas) or pancreas bifidum is extremely rare congenital malformation. This anatomical variant is characterized by an abnormal branching of the main pancreatic duct. This anomaly is generally not associated with abdominal pain or pancreatic disease. Most cases are asymptomatic, detected incidentally. Nevertheless, pancreas bifidum may cause acute pancreatitis [1]. Herein, we report the case of a 65-year-old female patient with a previous recurrent episode of acute pancreatitis. Patient had none clinical predisposing factors for acute pancreatitis. Abdominal MRI, including MRCP (MR cholangiopancreatography), was performed to better evaluation of the biliary tract and pancreatic parenchyma. MRCP (Figure 1) showed duplication of the major duct in the tail of the pancreas. Axial T2-weighted image (Figure 2) showed ventral and dorsal pancreatic buds with the typical fish tail appearance.
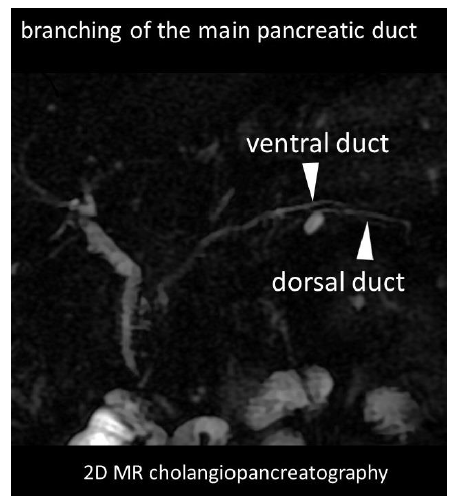
Figure 1: 2D MR cholangiopancreatography.
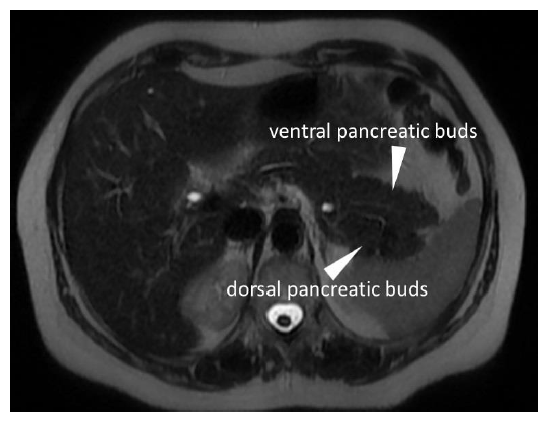
Figure 2: Axial T2-weighted image showing ventral and dorsal pancreatic buds with the typical fish tail appearance.
In the absence of clinical predisposing factors (alcohol or smoking history), in cases of acute pancreatitis, it is advisable to perform an abdominal MRI, including MRCP to rule out anatomical abnormalities as predisposing factors. Our case corroborates what reported in very few literature cases [2] of association between acute pancreatitis and bifid pancreas, besides displaying the typical MRI findings.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- APA Kahramanoglu Aksoy Evrim, Koklu Seyfettin, Öztürk Ömer, et al. An Unusual Cause of Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 45 (2016): e11-12.
- Koyasu S, Isoda H, Nakase H, et al. Bifid tail of the pancreas with localized acute pancreatitis. Magn Reson Med Sci 12 (2013): 315-318.
