Major Depression with Catatonic Features in Adolescent Remitted with Olanzapine, Sertraline and Haloperidol Decanoate
Article Information
Hesham Maged Mohammed abdelfatah
Egyptian Ministry of Health - General Secretariat for Mental Health and Addiction Treatment - El-Abbassia psychiatric Hospital, Cairo, EGYPT
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Hesham Maged Mohammed abdelfatah, Egyptian Ministry of Health - General Secretariat for Mental Health and Addiction Treatment - El-Abbassia psychiatric Hospital, Cairo, EGYPT
Received: 22 October 2021; Accepted: 01 November 2021; Published: 04 January 2022
Citation:
Hesham Maged Mohammed abdelfatah. Major Depression with Catatonic Features in Adolescent Remitted with Olanzapine, Sertraline and Haloperidol Decanoate. Journal of Psychiatry and Psychiatric Disorders 6 (2022): 001-007.
Share at FacebookAbstract
Catatonia is a complex neuropsychiatric syndrome that's often related to psychiatric, neurological and or medical disorders. so to diagnosis of catatonia, the clinical picture must be found by three or more of the subsequent symptoms; cataplexy, waxy flexibility, stupor, agitation, mutism, negativism, posturing, mannerisms, stereotypies, grimacing, echolalia, and echopraxia. I present a case of adolescent 14-year-old Male who presented to the my private clinic with a one month history of feeling depressed, anhedonia, hopeless, helpless, and worthless, related to poor sleep, poor concentration, low energy, markedly reduced in the appetite with significant weight loss, Patient exhibited symptoms like mutism, hyper-extension of spine, clinching of jaw, psychomotor retardation which suggested diagnosis of catatonia at the background of major depressive disorder not responding to treatment described by adolescent department of mental hospital, This case report demonstrates the necessity for a high index of suspicion and early diagnosis of catatonia in psychiatric patients given the high morbidity and mortality that's related to this condition if delayed or undiagnosed.
Keywords
Major depressive disorders; Catatonia; Divorce; Adolescent; Maternal deprivation
Major depressive disorders articles; Catatonia articles; Divorce articles; Adolescent articles; Maternal deprivation articles
Clock Drowning Test articles Clock Drowning Test Research articles Clock Drowning Test review articles Clock Drowning Test PubMed articles Clock Drowning Test PubMed Central articles Clock Drowning Test 2023 articles Clock Drowning Test 2024 articles Clock Drowning Test Scopus articles Clock Drowning Test impact factor journals Clock Drowning Test Scopus journals Clock Drowning Test PubMed journals Clock Drowning Test medical journals Clock Drowning Test free journals Clock Drowning Test best journals Clock Drowning Test top journals Clock Drowning Test free medical journals Clock Drowning Test famous journals Clock Drowning Test Google Scholar indexed journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale articles Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale Research articles Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale review articles Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale PubMed articles Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale PubMed Central articles Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale 2023 articles Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale 2024 articles Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale Scopus articles Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale impact factor journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale Scopus journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale PubMed journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale medical journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale free journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale best journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale top journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale free medical journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale famous journals Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale Google Scholar indexed journals Major depressive disorders articles Major depressive disorders Research articles Major depressive disorders review articles Major depressive disorders PubMed articles Major depressive disorders PubMed Central articles Major depressive disorders 2023 articles Major depressive disorders 2024 articles Major depressive disorders Scopus articles Major depressive disorders impact factor journals Major depressive disorders Scopus journals Major depressive disorders PubMed journals Major depressive disorders medical journals Major depressive disorders free journals Major depressive disorders best journals Major depressive disorders top journals Major depressive disorders free medical journals Major depressive disorders famous journals Major depressive disorders Google Scholar indexed journals Catatonia articles Catatonia Research articles Catatonia review articles Catatonia PubMed articles Catatonia PubMed Central articles Catatonia 2023 articles Catatonia 2024 articles Catatonia Scopus articles Catatonia impact factor journals Catatonia Scopus journals Catatonia PubMed journals Catatonia medical journals Catatonia free journals Catatonia best journals Catatonia top journals Catatonia free medical journals Catatonia famous journals Catatonia Google Scholar indexed journals Divorce articles Divorce Research articles Divorce review articles Divorce PubMed articles Divorce PubMed Central articles Divorce 2023 articles Divorce 2024 articles Divorce Scopus articles Divorce impact factor journals Divorce Scopus journals Divorce PubMed journals Divorce medical journals Divorce free journals Divorce best journals Divorce top journals Divorce free medical journals Divorce famous journals Divorce Google Scholar indexed journals Adolescent articles Adolescent Research articles Adolescent review articles Adolescent PubMed articles Adolescent PubMed Central articles Adolescent 2023 articles Adolescent 2024 articles Adolescent Scopus articles Adolescent impact factor journals Adolescent Scopus journals Adolescent PubMed journals Adolescent medical journals Adolescent free journals Adolescent best journals Adolescent top journals Adolescent free medical journals Adolescent famous journals Adolescent Google Scholar indexed journals Maternal deprivation articles Maternal deprivation Research articles Maternal deprivation review articles Maternal deprivation PubMed articles Maternal deprivation PubMed Central articles Maternal deprivation 2023 articles Maternal deprivation 2024 articles Maternal deprivation Scopus articles Maternal deprivation impact factor journals Maternal deprivation Scopus journals Maternal deprivation PubMed journals Maternal deprivation medical journals Maternal deprivation free journals Maternal deprivation best journals Maternal deprivation top journals Maternal deprivation free medical journals Maternal deprivation famous journals Maternal deprivation Google Scholar indexed journals schizophrenia articles schizophrenia Research articles schizophrenia review articles schizophrenia PubMed articles schizophrenia PubMed Central articles schizophrenia 2023 articles schizophrenia 2024 articles schizophrenia Scopus articles schizophrenia impact factor journals schizophrenia Scopus journals schizophrenia PubMed journals schizophrenia medical journals schizophrenia free journals schizophrenia best journals schizophrenia top journals schizophrenia free medical journals schizophrenia famous journals schizophrenia Google Scholar indexed journals psychiatry articles psychiatry Research articles psychiatry review articles psychiatry PubMed articles psychiatry PubMed Central articles psychiatry 2023 articles psychiatry 2024 articles psychiatry Scopus articles psychiatry impact factor journals psychiatry Scopus journals psychiatry PubMed journals psychiatry medical journals psychiatry free journals psychiatry best journals psychiatry top journals psychiatry free medical journals psychiatry famous journals psychiatry Google Scholar indexed journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome articles neuroleptic malignant syndrome Research articles neuroleptic malignant syndrome review articles neuroleptic malignant syndrome PubMed articles neuroleptic malignant syndrome PubMed Central articles neuroleptic malignant syndrome 2023 articles neuroleptic malignant syndrome 2024 articles neuroleptic malignant syndrome Scopus articles neuroleptic malignant syndrome impact factor journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome Scopus journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome PubMed journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome medical journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome free journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome best journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome top journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome free medical journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome famous journals neuroleptic malignant syndrome Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
Abbreviations
CDT: Clock Drowning Test; BFCRS: Bush- Francis Catatonia Rating Scale
1. Introduction
Catatonia could be a complex neuropsychiatric syndrome that's often related to psychiatric, neurological and or medical conditions. in step with the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition (DSM-5), catatonia is characterized by three or more of the subsequent symptoms; cataplexy, waxy flexibility, stupor, agitation, mutism, negativism, posturing, mannerisms, stereotypies, grimacing, echolalia, echopraxia [1]. Historically, catatonia was related to schizophrenia and classified as a sub-type of the disorder but there's increasing evidence that catatonia can occur in patients with mood disorders, neurologic disease, and other medical conditions [2]. However, recent studies show that the prevalence of catatonia among schizophrenic patients ranges between 4% – 15% [3, 4].
Although the symptoms of catatonia are distinct, studies have shown significant under-diagnosis or missed diagnosis of this condition. during a retrospective study drained a medical inpatient unit between 2011 and 2013 using DSM-5, of the total of 133 cases satisfying the diagnosis of catatonia, 79 were undiagnosed. The study found that psychiatry consultation decreases the chances of under diagnosis, whereas agitation, grimacing or echolalia increases the chances of under-diagnosis.The prevalence of catatonia differs in several medical settings ranging from 5%-18% on inpatient psychiatric units,12% in drug-naive patients with first-episode psychosis, 3.3 on a neurology/neuropsychiatric tertiary care inpatient units, 1.6% to 1.8% on psychiatry consultation-liaison services, 8.9% in elderly patients and three.8% on treatment units [5]. It has been reported that catatonia carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality, partly thanks to failure of timely recognition and initiation of appropriate treatment [6].
Catatonia appears to be have multiple complications illustrated in Table [1] on of these complications was neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which has a death rate of roughly 10% and can be clinically difficult to differentiate from malignant catatonia [7]. Catatonia occurs frequently in acutely ill patients [8]. Some studies have also reported catatonic syndrome in children and adolescents [9]. Prompt diagnosis and adequate treatment are very crucial within the management of catatonia to avoid poor outcomes. Most times, the diagnosis of catatonia is missed because a number of the symptoms of catatonia overlap with other psychiatric disorders, and this may well be life-threatening to the patient [10]. Symptoms and syndromes that should be differentiated from catatonia include; extrapyramidal side effects, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, non-convulsive epilepsy, abulia, and locked-in syndrome.
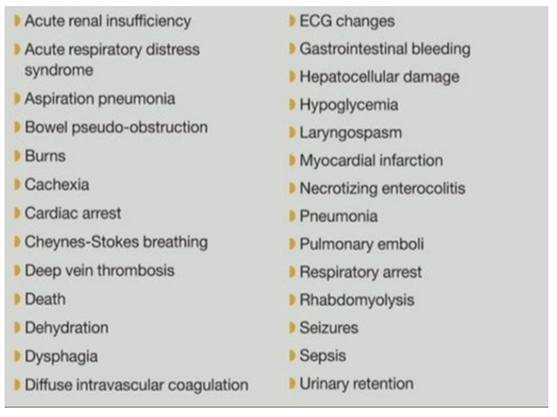
Figure 1: Medical Complications of catatonia.
2. Case Presentation
Patient is a 14-year-old Egyptian nationality, student , His father financially poor and was separated from his mother from 5 years ago and married from another woman no reported family psychiatric history? he was brought to my private clinic by his father and the stepmother. activated feeling depressed. Upon evaluation, he was poorly groomed and appeared unkempt.
Patient reported feeling depressed, anhedonia, hopeless, helpless, and worthless, associated with significant weight loss due to lack of appetite. He also reported poor sleep, poor concentration, low energy, his father reported that this symptoms appeared from two months when the patient asked to see his mother but she refused that because she married and the stepfather don't want him in his home,
Patient could not recall the exact number of weeks, the pervious psychiatric history recorded that's from 3 years ago the patient was admitted to the children psychatric unit from for stabilization During his inpatient stay, the patient continued to endorse poor appetite, low energy, depressed mood, anhedonia, feelings of hopelessness and a motivation.
There was observable psychomotor retardation. he was started on olanzapine 5 mg orally twice daily for insomnia and agitation and refused eating and sertraline 50mg once daily for depressed mood, appetite, and sleep. and there was a decision to given him ECT therapy, but due to his age 11 years at this time and he was starting to eat and spoke, the final decision after making staff consultation was continued on the medical treatment by the previous drugs only for 3 months, the symptoms disappeared gradually and he began to eat and spoke with minimal psychomotor retardation, but refused to go to school that's leading to negative effects of education achievement, and due to his strong attachment to his Mather but in the same times there was Mather refused due to her husband, from two month ago the same attack returns but with exaggerated symptoms with worsening psychomotor retardation, depressed mood, and anhedonia. Laboratory investigation was performed which revealed evidence hypoglycemia and dehydration. The patient father attempted to internal medicine doctor that use a nasogastric tube inserted to feeding, The patient became completely mute and stared more often. He was giving haloperidol 5 mg IM injection once daily for 3 days and Sertraline 50 mg tablet once daily and olanzapine 5 mg twice daily, the appetite improved and he took his medications without clenching his teeth. He was able to mobilize independently. The haloperidol changes to the Decanoate form one's per mouth, he began to participate in activity like Praying and playing football, eating well, speaking well, elevated mood and reactive affect, partial insight and fair judgment, he was under CBT therapy including his father and his mother now he was negative for catatonia. The patient’s weight improves, his depressive symptoms had significantly improved, and his affect was brighter. It is worth noting that the patient had various specialty consultations during his inpatient stay and in his father home from Gastroenterology, Neurology, Surgical, Chest and Internal medicine, none provided a medical diagnosis. Thyroid function test, complete blood count, complete metabolic panel, lipid panel, urine toxicology screen, CT Brain and EEG and ECG was done on admission and values were within normal limits.
3. Discussion
This report described an in depth clinical course of catatonia during a patient with major major affective disorder (MDD). This patient was initially thought to own only clinical features implicative MDD in line with the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria. However, his symptoms when the correct diagnosis was made was improved. This case corroborates existing scientific evidence of the high prevalence of missed, delayed or under-diagnosis of catatonia. It appears that catatonia can mask the treatment outcome if catatonia may be a component of another psychiatry diagnosis; hence improvement in other depressive symptoms couldn't be appreciated catatonia may be a component of the emotional disorder. within the psychiatric unit, catatonia is becoming increasingly related to mood disorder [11]. Overall, the study indicated that the occurrence of catatonia ranges from 5.3% to 19% within the psychiatric unit. Catatonia was revealed to be more severe within the early stages of illness, in those with prior episodes of catatonia and within the pediatric population [12].
This case report demonstrated the importance of a high index of clinical suspicion, proper physical and mental status assessment in diagnosing catatonia that's co-occurring with another psychological state. Our patient’s diagnosis was delayed and missed by both the medical and psychiatric team due to the low index of suspicion, hence was easily overlooked. Another possible reason is that the overlapping symptoms of catatonia with MDD, especially psychomotor retardation. These points to the requirement for early screening of Catatonia in high risk individuals. Diagnosing catatonia could be a major challenge for 2 parts. First, there aren't any subjective findings on laboratory or imaging studies, that the diagnosis depends solely on clinical assessments and rating scales. Second, there's nearly always an associated medical, neurological or psychiatric condition. Despite the aforementioned challenges, an in depth assessment is typically enough to create a diagnosis because it could be a clinical diagnosis. a standard finding on examination is an abnormality within the Clock Drawing Test (CDT). This may be suggestive impaired cognition in Catatonia. CDT becomes very useful in situations where complex neuropsychological evaluation is impossible [13].
Rating scales like BFCRS are used over the years for screening purposes, to quantify the severity of catatonia moreover as evaluate response to treatment [14]. There are several rating scales available for clinical use, but BFCRS is usually used because it's simple to administer and because of its reliability and validity [15]. Although the precise explanation for catatonia is unclear, changes in Gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate signaling has been postulated as a causative factor 13 Also, imaging studies in psychotic patients with hypokinetic catatonia revealed increased neural activity within the premotor areas 11. Despite the poor understanding of the etiology of catatonia, patients with this condition respond rapidly to benzodiazepine (BZD) and ECT. However, in our case where BZD is ineffective, and ECT unavailable, patients may like Typical, atypical antipsychotics, and SSRI [16, 17] MDD patients with catatonia have a remission rate of 80% in adults and 65% in children [18].
4. Conclusion
Catatonia is treatable if diagnosed early and accurately. But if left untreated, it could lead to high morbidity and mortality. Therefore, physicians must have a high index of suspicion when managing patients with features of catatonia and if possible, a psychiatrist should be consulted. Also this case study emphasizes the importance of family cohesion and the adverse effects of divorce on children which become the main stressors for children and adolescents mental illness.
Informed Consent
Patient and patients relative was informed and taken written consent from patient’s relative before initiation of case report.
Funding Details
None.
Acknowledgments
None.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing (2013).
- Walther S, Strik W. Catatonia. CNS spectrums 21 (2016): 341-348.
- Kleinhaus K, Harlap S, Perrin MC, et al. Catatonic schizophrenia: a cohort prospective study. Schizophr Bull 38 (2010): 331-337.
- Stuivenga M, Morrens M. Prevalence of the catatonic syndrome in an acute inpatient sample. Front Psychiatry 5 (2014): 174.
- Llesuy JR, Medina M, Jacobson KC, et al. Catatonia underdiagnosis in the general hospital. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 30 (2018): 145-151.
- Heekin RD, Bradshaw K, Calarge CA. First known case of catatonia due to cyclosporine A-related neurotoxicity in a pediatric patient with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. BMC Psychiatry 19 (2019): 123.
- Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World Journal of Psychiatry 6 (2016): 391-398.
- Fink M, Taylor MA. The catatonia syndrome: forgotten but not gone. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66 (2009): 1173-1177.
- Jhawer H, Sidhu M, Patel RS. Missed Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder with Catatonia Features. Brain Sci 9 (2019): 31.
- Jahan S. Catatonia in a 17-year-old Male Patient with Bipolar Disorder, a Case Study. CNS spectrums 24 (1983): 217-217.
- Walther S, Stegmayer K, Wilson JE, et al. Structure and neural mechanisms of catatonia. The Lancet Psychiatry 6 (2019): 610-611.
- Subramaniyam BA, Muliyala KP, Hara SH, et al. Prevalence of catatonic signs and symptoms in an acute psychiatric unit from a tertiary psychiatric center in India. Asian Journal of Psychiatry 44 (2019):13-17.
- Medina M, Cooper JJ. Utility of the Clock Drawing Test in the Assessment of Catatonia. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 31 (2018): 89-91.
- Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry 6 (2016): 391.
- Sienaert P, Rooseleer J, De Fruyt J. Measuring catatonia: a systematic review of rating scales. J Affect Disord 135 (2011): 1-9.
- Azzazy S, Hansen-Cook S, Carroll T. When a Benzodiazepine Can Help Save a Life: Periodic and Malignant Catatonia in an Aging Veteran. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 26 (2018): S162.
- Beach SR, Gomez-Bernal F, Huffman JC, et al. Alternative treatment strategies for catatonia: a systematic review. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 48 (2017):1-19.
- Jhawer H, Sidhu M, Patel RS. Missed Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder with Catatonia Features. Brain Sci 9 (2019): 31.
