Gassless Single-Port Retroperitoneoscopic Surgery for Urologic Disease: Case Series Reports
Article Information
Chen-Che Lee1,2#, Kuo-Jen Lin1,2#, Pei-Shan Yang1,2, Chen-Pang Hou1,4, Yu-Hsiang Lin1,4, Horng-Heng Juang1,3, Phei-Lang Chang1,2, Chien-Lun Chen1,2, Ke-Hung Tsui1,2*
#Authors contributed equally
1Department of Urology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital at linkou, Taiwan
2School of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taiwan
3Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Kwei-shan, Tao-Yuan, Taiwan
4Graduate Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taiwan
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Ke-Hung Tsui, Department of Urology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital-Linkou, 5 Fu-Shing Street, Kweishan, Taoyuan, 333, Taiwan
Received: 03 August 2020; Accepted: 20 August 2020; Published: 28 August 2020
Citation: Chen-Che Lee, Kuo-Jen Lin, Pei-Shan Yang, Chen-Pang Hou, Yu-Hsiang Lin, Horng-Heng Juang, Phei-Lang Chang, Chien-Lun Chen, Ke-Hung Tsui. Gassless Single-Port Retroperitoneoscopic Surgery for Urologic Disease: Case Series Reports. Archives of Nephrology and Urology 3 (2020): 077-082.
Share at FacebookAbstract
Introduction: The effects of Gassless single port retroperitoneoscopic surgery with urologic diseaseremain unclear. In this retrospective review, we aim to elucidate the effect of the Gassless retroperitoneoscopy for urologic disease.
Methods: We retrospectively enrolled five consecutive patients who visited the urologic department for urologic disease from January 2016 to October 2016. All cases were followed up at least 12 months postoperatively. Of these, two renal mass, two adrenal tumors and one ureter stricture were reports.
Result: There were no significant differences between the characteristics of these groups. (p<0.05) The total complications and bleeding did not tend to difference to the discovered between the multiple port laparoscopic surgery. Postoperative length of stay and outcome were no difference then before data.
Conclusion: Our data revealed that Gassless single port retroperitoneoscopy surgery for urologic disease were achieved favorable outcomes for patients with urologic disease.
Keywords
Retroperitoneoscopy; Gassless; Urologic neoplasm; Surgery; Single port
Retroperitoneoscopy articles, Gassless articles, Urologic neoplasm articles, Surgery articles, Single port articles
Retroperitoneoscopy articles Retroperitoneoscopy Research articles Retroperitoneoscopy review articles Retroperitoneoscopy PubMed articles Retroperitoneoscopy PubMed Central articles Retroperitoneoscopy 2023 articles Retroperitoneoscopy 2024 articles Retroperitoneoscopy Scopus articles Retroperitoneoscopy impact factor journals Retroperitoneoscopy Scopus journals Retroperitoneoscopy PubMed journals Retroperitoneoscopy medical journals Retroperitoneoscopy free journals Retroperitoneoscopy best journals Retroperitoneoscopy top journals Retroperitoneoscopy free medical journals Retroperitoneoscopy famous journals Retroperitoneoscopy Google Scholar indexed journals Gassless articles Gassless Research articles Gassless review articles Gassless PubMed articles Gassless PubMed Central articles Gassless 2023 articles Gassless 2024 articles Gassless Scopus articles Gassless impact factor journals Gassless Scopus journals Gassless PubMed journals Gassless medical journals Gassless free journals Gassless best journals Gassless top journals Gassless free medical journals Gassless famous journals Gassless Google Scholar indexed journals Urologic neoplasm articles Urologic neoplasm Research articles Urologic neoplasm review articles Urologic neoplasm PubMed articles Urologic neoplasm PubMed Central articles Urologic neoplasm 2023 articles Urologic neoplasm 2024 articles Urologic neoplasm Scopus articles Urologic neoplasm impact factor journals Urologic neoplasm Scopus journals Urologic neoplasm PubMed journals Urologic neoplasm medical journals Urologic neoplasm free journals Urologic neoplasm best journals Urologic neoplasm top journals Urologic neoplasm free medical journals Urologic neoplasm famous journals Urologic neoplasm Google Scholar indexed journals Surgery articles Surgery Research articles Surgery review articles Surgery PubMed articles Surgery PubMed Central articles Surgery 2023 articles Surgery 2024 articles Surgery Scopus articles Surgery impact factor journals Surgery Scopus journals Surgery PubMed journals Surgery medical journals Surgery free journals Surgery best journals Surgery top journals Surgery free medical journals Surgery famous journals Surgery Google Scholar indexed journals Single port articles Single port Research articles Single port review articles Single port PubMed articles Single port PubMed Central articles Single port 2023 articles Single port 2024 articles Single port Scopus articles Single port impact factor journals Single port Scopus journals Single port PubMed journals Single port medical journals Single port free journals Single port best journals Single port top journals Single port free medical journals Single port famous journals Single port Google Scholar indexed journals urologic disease articles urologic disease Research articles urologic disease review articles urologic disease PubMed articles urologic disease PubMed Central articles urologic disease 2023 articles urologic disease 2024 articles urologic disease Scopus articles urologic disease impact factor journals urologic disease Scopus journals urologic disease PubMed journals urologic disease medical journals urologic disease free journals urologic disease best journals urologic disease top journals urologic disease free medical journals urologic disease famous journals urologic disease Google Scholar indexed journals retroperitoneoscopy articles retroperitoneoscopy Research articles retroperitoneoscopy review articles retroperitoneoscopy PubMed articles retroperitoneoscopy PubMed Central articles retroperitoneoscopy 2023 articles retroperitoneoscopy 2024 articles retroperitoneoscopy Scopus articles retroperitoneoscopy impact factor journals retroperitoneoscopy Scopus journals retroperitoneoscopy PubMed journals retroperitoneoscopy medical journals retroperitoneoscopy free journals retroperitoneoscopy best journals retroperitoneoscopy top journals retroperitoneoscopy free medical journals retroperitoneoscopy famous journals retroperitoneoscopy Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Introduction
Single port retroperitoneoscopy is used commonly worldwide in urologic surgery. It is a minimal invasive laparoscopic procedure using endoscopy, widely applied in almost all urologic organ [1, 2], and also Gynecology organs [3, 4]. Recently, cases of partial nephrectomy or non-ischemic partial nephrectomy using this skill have also been reported [5-7]. This surgery has good post-operative outcomes while reducing the invasiveness of conventional open surgery and multiple trocar scars [5, 8, 9]. Thus, many medical centers worldwide have been developing this technique in urologic surgery ever since 2008 [7-11]. In this study, we pointed out that old age and poor performance patients whose condition is not suitable for infusion of CO2 on the peritoneal cavity. We propose cases to share new surgical methods for urologic disease. This case series study is aimed to evaluate the surgical outcomes of patients with Gassless single port retroperitoneoscopy surgery in urologic disease. To the best of our knowledge, these is no study that measurements the effect of gassless single port retroperitoneoscopy surgery in urologic disease.
2. Case Series Reports
From January 2016 to October 2016, a total of 5 patients received Gassless single port retroperitoneoscopy surgery in our Chang Gung Memorial hospital-LinKo. The including criteria were: (1) age more than 20 years old or older; (2) have urologic disease which needed surgery; (3) without medical history of complication diseases (Table 1). In the renal surgery group, two renal tumor patients receiving partial nephrectomy, off these, one right 5cm cystic tumor and the other left 2 cm solid tumor, as shown in Figure 1. One left ureter stricture with hydronephrosis was undergone ureteroureterostomy surgery and two adrenal tumor were undergone for adrenalectomy, with image shown in Figure 2. The operative time is from 90 to 186 minutes, and the patients were hospitalized for 3 to 7 days. Every patient underwent thorough exams including blood tests and image studies by CT, with clear lesion sights as seen in figure 1 and 2. All of the patients were under general anesthesia with lateral decubitus position. 2-D rigid laparoscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) or 3-D head-mounted display system (Shinko Optical, Tokyo, Japan, and Endoeye flex 3D deflectable videoscope, Olympus) were used during surgery.
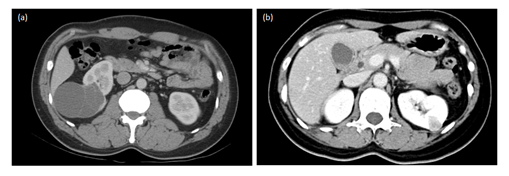
Figure 1: CT scan image of renal tumor. (a) right cystic 5 cm tumor; (b) left 2 cm solid tumor.
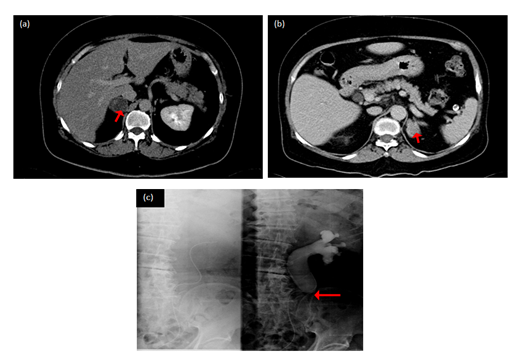
Figure 2: CT scan image of adrenal tumor and ureter stricture. (a,b) adrenal tumor; (c) left upper ureter stricture.
|
Patient number |
5 |
|
Age (range, SD) |
49.9 (20-66) |
|
Male/Female |
4/1 |
|
ASA score > III, n (%) |
1 (20%) |
|
Anesthesia |
General |
|
Kidney tumor (size) /no |
5 cm / 2 cm (2) |
|
Adrenal tumor (size) /no |
2.5 cm / 2 cm (2) |
|
Ureter stricture with Hydronephrosis (No) |
1 |
Table 1: Pre-operative data of the patients (n = 5).
2.1 Surgical technique
All patients received single port retroperitoneoscopy placed in lateral decubitus position. A 4 cm incision wound was made under 12th rib (Figure 3) and minlaparotomy into retroperitoneal space. Once we established 4 cm retroperitoneal space, and then enter the retroperitoneal space. We used 10 mm trocar one and 5 mm trocar two instrument for the surgery. In partial nephrectomy for renal tumor, Gerota fascia was opened and the tumor located. After dissecting the ureter and renal pedicle and exposuring the tumor, ultrasound was used to define the margin, depth and size of the tumor. Non-ischemia partial nephrectomy method was used without clamping renal pedicles. Ultrasonic coagulating device (Harmonic; Ethicon, Cincinnati, OH, USA) was used for excision of the tumor with a margin of at least 0.5 cm. In the adrenal and ureter group, retroperitoneal approach was used with same methods.
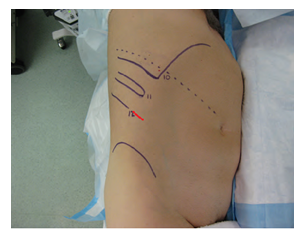
Figure 3: 4 cm incision wound for single port with patient placed as lateral decubitus position.
3. Result
A total of five patients with received Gassless single-port retroperitoneoscopy surgery. The mean age was 67 years in the surgical group, respectively. In both cases of partial nephrectomy for renal tumor, negative margin was achieved with blood loss less than 250 ml. The pathological report of renal tumor showed T1 and complete resection. Drainage tube was removed after 5 days and length of hospital stay was around 7 days. There was neither blood transfusion nor complication. Both patients are now under regular clinical follow up with no renal function deterioration. Both cases of adrenalectomy and the case of ureteroureterostomy were performed smoothly with also free margin and 10 to 50 ml blood loss. All 3 patients recovered well and were discharged after 3 days of hospitalization. According to the Gassless retroperitoneoscopy surgery and the practice of our department, a week of medication treatment was given before further follow up.
4. Discussion
Minimal invasive surgery is the mainstream surgery in the world [10]. If the patient has cardiovascular disease, there is no way to used CO2 into the peritoneal cavity for long -time surgery. Gassless single port retroperitoneoscopy is an effective surgery allowing the patient to achieve fast recovery and return to normal daily activity. This case series reports are an application of our experience to share and that the procedure is feasible. In non-ischemia partial nephrectomy patient, blood loss is controlled to less than 250 ml with no blood transfusion needed and no cases of complication were reported. The mean operative time is 3 hours and means hospital stay is less or equally to 7 days. Blood loss was less than 50 ml adrenalectomy and ureteroureterostomy with hospital stay of 3 days, all without complication. This indicates that apart from old age, poor performance and not suitable for infusion CO2 to the intraperitoneal space. It provides another option when considering minimal invasive surgery. From our experience, this is the development of a new surgical technology for urologic disease. Gassless retroperitoneoscopic surgery is a safe, effective and worth promoting surgery. This new surgical procedure is not just a safe operation but also a patient whose condition is not suitable for infusion of CO2 on the peritoneal cavity. Furthermore, more cases are needed for further evaluation of the procedure in the future.
5.Limitations
There are some limitations in this study first, only five cases were included in this study; therefore, we do not know whether more cases will cause the same effect in younger and old patients. To study the clinically significant risks requires a much larger sample size.
6.Conclusions
Gassless single-port retroperitoneoscopic surgery is a safe, effective and worth promoting surgery. In patients with a urologic disease who considered received laparoscopic surgery and patient who are high risk for CO2 infusion, Gassless single-port retroperitoneoscopy surgery may did not worsen outcome results. Furthermore, more cases are needed for further evaluation of the procedure in the future.
Acknowledgment
This report was not funded by any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author Contributions
KH designed the study, contributed to collect, analyze and interpret data, and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. CC contributed to interpret the data, and assisted in the preparation of the manuscript. All authors contributed to data analysis, drafting and revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- Clayman RV, Kavoussi LR, Soper NJ, et al. Laparoscopicnephrectomy. N. Engl. J. Med 324 (1991): 1370-1371.
- Guillonneau B, Vallancien G. Laparoscopic radicalprostatectomy: initial experience and preliminaryassessment after 65 operations. Prostate 39 (1999): 71-75.
- Tae-Hyun Kim, Chul Jung Kim, Tae-Joong Kim, et al. Retroperitoneal Approach in Single-Port Laparoscopic Hysterectomy. JSLS 20 (2016): e2016.00001.
- Moito Iijima, Shigenori Hayashi, Yusuke Kobayashi, et al. Laparoscopic Surgery for Ovarian Cyst Infection with Avoidance of Ureteral Injury and Uterine Perforation following Intrauterine Insemination after Abdominal Modified Radical Trachelectomy. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol (2019): 8607417.
- Kageyama Y, Kihara K, Yokoyama M, et al. Endoscopicminilaparotomy partial nephrectomy for solitary renal cellcarcinoma smaller than 4 cm. Jpn J. Clin. Oncol 32 (2002): 417-421.
- Kaouk JH, Goel RK. Single-port laparoscopic and robotic partial nephrectomy. Eur Urol 55 (2009): 1163-1169.
- Hou CP1, Lin YH, Hsu YC, et al. Using a Harmonic Scalpel "Drilling and Clamping" Method to Implement Zero Ischemic Robotic-assisted Partial Nephrectomy: An Observation Case Report Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 95 (2016): e2349.
- Kihara K, Kobayashi T, Kawakami S, et al. Minimum incision endoscopic surgery (MIES) in Japanese urology: results of adrenalectomy, radical nephrectomy and radical prostatectomy. Aktuelle Urol 41 (2010): S15-S19.
- Kihara K, Kawakami S, Fujii Y, et al. Gasless single-port access endoscopic surgery in urology: minimum incision endoscopic surgery, MIES. Int. J. Urol 16 (2009): 791-800.
- Gettman MT, Blute ML, Chow GK, et al. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: technique and initial clinical experience with DaVinci robotic system. Urology 64 (2004): 914-918.
- Motzer RJ, Jonasch E, Agarwal N, et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: kidney cancer, version 2.2014. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw 12 (2014): 175-182.
